Tutorial Unit Plugin With Rodin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Update installation screencast link |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Tutorial]] | [[Category:Tutorial]] | ||
[[Category:User Manual]] | [[Category:User Manual]] | ||
[[Category:Physical Units Plugin]] | |||
This tutorial describes, how ProB's integrated plugin for unit analysis can be used with Event-B machines from inside the Rodin platform. This includes | This tutorial describes, how ProB's integrated plugin for unit analysis can be used with Event-B machines from inside the Rodin platform. This includes | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
== Installing Physical Units Support for ProB for Rodin == | == Installing Physical Units Support for ProB for Rodin == | ||
You can follow the [[Tutorial Rodin First Step|First Steps Instructions]] or the [ | You can follow the [[Tutorial Rodin First Step|First Steps Instructions]] or the [[Installation#Installation Instruction for ProB (Rodin Plugin)|Screencast]] to install ProB for Rodin. | ||
In addition to the "ProB for Rodin2" plugin there is a "ProB for Rodin2 - Physical Units Support" plugin at out Rodin update site. You have to install both to enable physical units support for Rodin. | In addition to the "ProB for Rodin2" plugin there is a "ProB for Rodin2 - Physical Units Support" plugin at out Rodin update site. You have to install both to enable physical units support for Rodin. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
Units can be supplied in two forms: | Units can be supplied in two forms: | ||
* by using an alias like "m", "cm", "mps" and so on, | * by using an alias like "m", "cm", "mps" and so on, | ||
* or by using an Event-B Expression in an SI unit compatible form, like 10^2 * m^2. | * or by using an Event-B Expression in an SI unit compatible form, like "10^2 * m^2". | ||
== Starting the Analysis == | == Starting the Analysis == | ||
Latest revision as of 16:05, 3 February 2021
This tutorial describes, how ProB's integrated plugin for unit analysis can be used with Event-B machines from inside the Rodin platform. This includes
- Annotating variables with their physical unit,
- Infer the unit of variables without an annotation,
- Detect incorrect usage of units, like addition of differently annotated variables.
Both the plugin itself and the bridge to Rodin are a work in progress. Preliminary support is available in the nightly builds of ProB for Rodin and will be merged in the regular releases in the future.
We assume that you have a general understanding of Event-B and the usage of ProB / Rodin.
Installing Physical Units Support for ProB for Rodin
You can follow the First Steps Instructions or the Screencast to install ProB for Rodin.
In addition to the "ProB for Rodin2" plugin there is a "ProB for Rodin2 - Physical Units Support" plugin at out Rodin update site. You have to install both to enable physical units support for Rodin.
Attaching Physical Units to Variables and Constants
Once both plugins are installed, ProB allows to annotate both variables and constants with physical units:

We store the user supplied unit and the units inferred by ProB as a new attribute in the Rodin database.
Units can be supplied in two forms:
- by using an alias like "m", "cm", "mps" and so on,
- or by using an Event-B Expression in an SI unit compatible form, like "10^2 * m^2".
Starting the Analysis
The supplied units can now be used by ProB to infer missing units, verify the supplied units and detect unit errors. To start the analysis use the context menu of the machine / context you want to analyse:
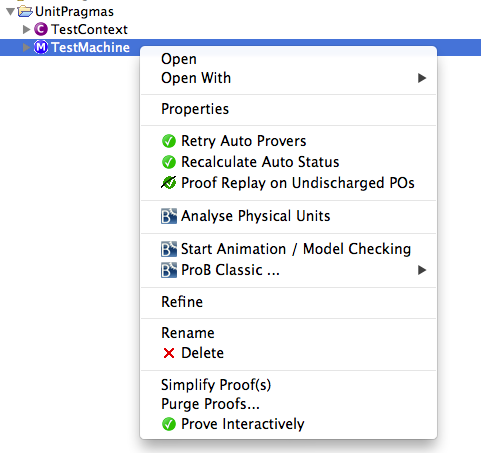
Necessary machines and contexts will be translated and passed to ProB. Once the analysis is finished, the "inferred unit" text fields are filled with the resulting units.
Possible Errors
Inside the Rodin Errors view, several errors might occur:
- An invalid unit has been supplied. Please check your input to the corresponding "Physical Unit" attribute.
- Multiple units have been inferred for a variable or constant.
Furthermore, we output a warning if no unit could be inferred for a variable or constant.