Tutorial Understanding the Complexity of B Animation
We assume that you grasped the way that ProB setups up the initial states of a B machine as outlined in Tutorial Setup Phases.
In this lesson, we examine the complexity of animation of B models in general, how ProB solves this problem and what the ramification for users are.
Undecidability
In general, animation of a B model is undecidable. I.e., it is undecidable whether a solution to the PROPERTIES can be found, whether a valid INITIALISATION exists and whether an operation can be applied.
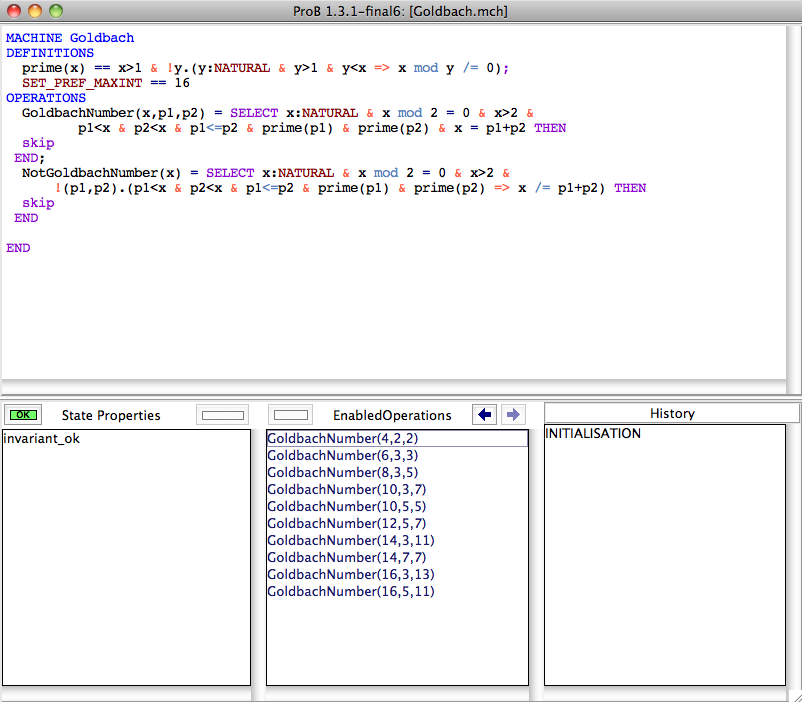
For example, the following B machine encodes Goldbach's conjecture (that every even number greater than 2 is a Goldbach number, i.e., it can be expressed as the sum of two primes):
MACHINE Goldbach
DEFINITIONS
prime(x) == x>1 & !y.(y:NATURAL & y>1 & y<x => x mod y /= 0)
OPERATIONS
GoldbachNumber(x,p1,p2) = SELECT x:NATURAL & x mod 2 = 0 & x>2 &
p1<x & p2<x & p1<=p2 & prime(p1) & prime(p2) & x = p1+p2 THEN
skip
END;
NotGoldbachNumber(x) = SELECT x:NATURAL & x mod 2 = 0 & x>2 &
!(p1,p2).(p1<x & p2<x & p1<=p2 & prime(p1) & prime(p2) => x /= p1+p2) THEN
skip
END
END
If the conjecture is true, then the operation NotGoldbachNumber is disabled; if the conjecture is false then it is enabled.
How does ProB overcome undecidability. First, it will enumerate integer variables only between MININT and MAXINT (unless the machine itself fixes the value to be outside of that range).
Hence, ProB will look for solutions to the parameter x of NotGoldbachNumber only until MAXINT. Hence, if we set MAXINT to 16 (adding a definiton SET_PREF_MAXINT == 16) we get the following picture after executing the INITIALISATION: