Handbook/ProB 2 UI
ProB2-UI
ProB2-UI is the new Java-based user interface for ProB.
Download
Download the latest version of ProB2-UI here. See also the release history.
The source code for ProB2-UI is available at https://github.com/hhu-stups/prob2_ui and can be built by following these instructions.
Features
Compared to the original UI based on Tcl/Tk, this new UI has some unique new features:
- Projects which store formal models, ProB preferences, and verification settings
- Load Rodin models from Rodin workspaces (without having to export them within Rodin)
- Managing and storing multiple trace files for a model, being able to replay all traces
- MC/DC test-case generation
- A view for managing LTL formulas for a model
- Visualisation of models using VisB and SVG graphics
- An integrated view for all dot-based graph visualisations (state space, machine hierarchy, formulas, projection diagrams, enabling graphs, event refinement hierarchy, ....)
- An integrated view to access all table based statistics (event coverage, MC/DC coverage, read-write matrices, WD POs, ...)
- A multi-language interface, currently providing English, French, German and Russian
We have developed a small
video highlighting the core features (also on YouTube) on a model the from visb-visualisation-examples:
Paper/Citing
Paper: Springer Link, ResearchGate
BibTeX citation:
@InProceedings{prob2ui,
author="Bendisposto, Jens
and Gele{\ss}us, David
and Jansing, Yumiko
and Leuschel, Michael
and P{\"u}tz, Antonia
and Vu, Fabian
and Werth, Michelle",
editor="Lluch Lafuente, Alberto
and Mavridou, Anastasia",
title="ProB2-UI: A Java-Based User Interface for ProB",
booktitle="Formal Methods for Industrial Critical Systems",
year="2021",
publisher="Springer International Publishing",
address="Cham",
pages="193--201",
abstract="ProB2-UI is a modern JavaFX-based user interface for the animator, constraint solver, and model checker ProB. We present the main features of the tool, especially compared to ProB's previous user interfaces and other available tools for B, Event-B, and other formalisms. We also present some of ProB2-UI's history as well as its uses in the industry since its release in 2019.",
isbn="978-3-030-85248-1"
}
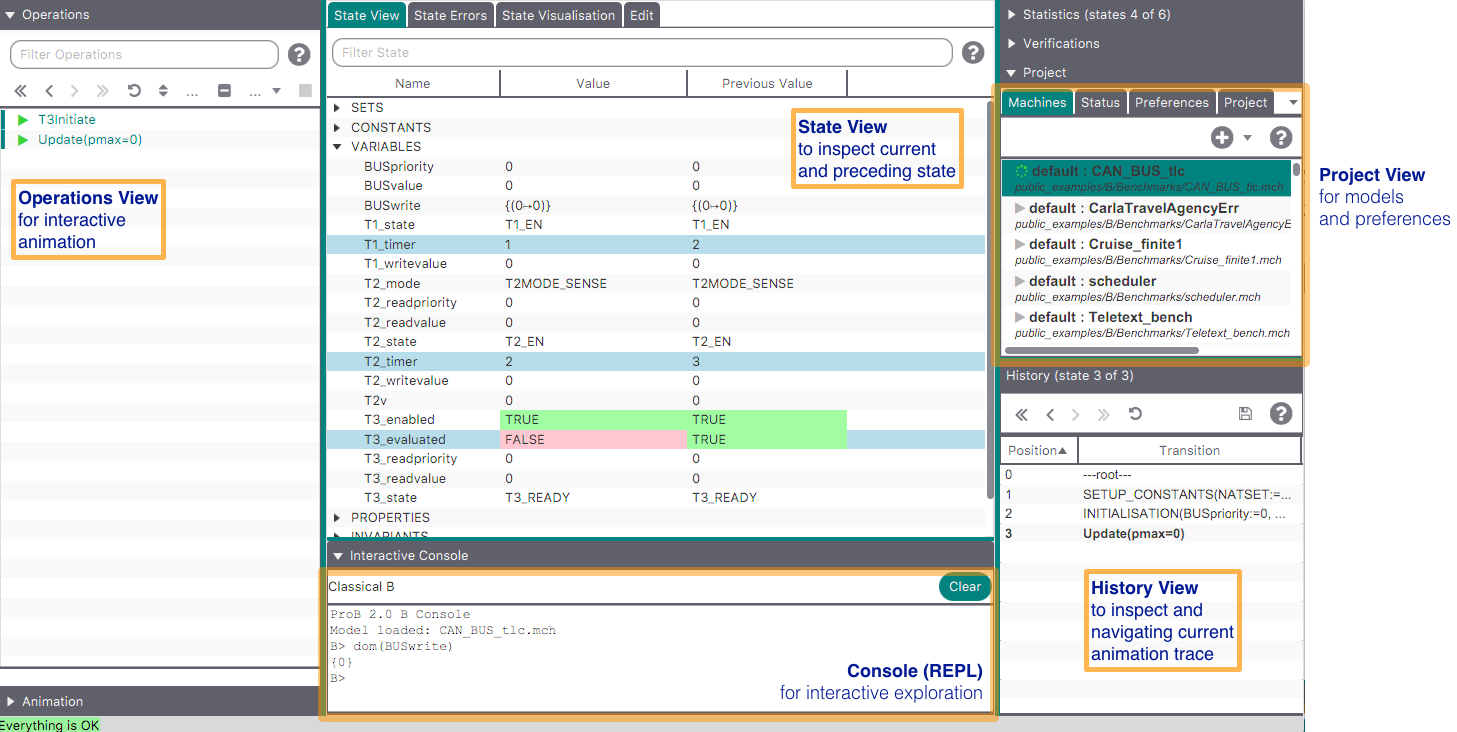
The ProB2-UI Main Window
By default the main window is split into three vertical panes (see below).
- In the left pane, the Operations view , showing the operations whose preconditions and guards are true in this state (the view also uses a blue circular arrow icon when an operation does not change the state);
- In the middle the State View, containing the current state of the B machine, listing e.g., the current values of the machine variables;
- In the right pane there are a variety of subviews, which can be activated:
The ProB2-UI Main Menu Bar
The menu bar contains the various commands to access the features of ProB. It includes the menus
- File,
- Edit,
- Formula,
- Consoles,
- Perspectives,
- View,
- Window and
- Help
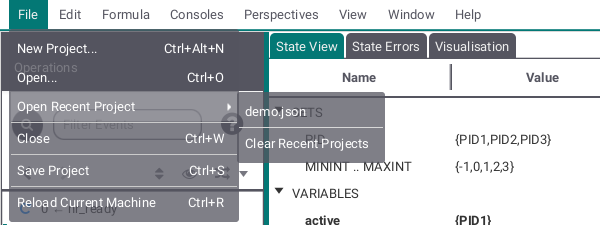
The File submenu allows you to create a new Project, open an existing project or a machine, open recent projects shown as list and/or clear the list of recent projects, close the ProB2-UI, save your project or reload the currently running machine.
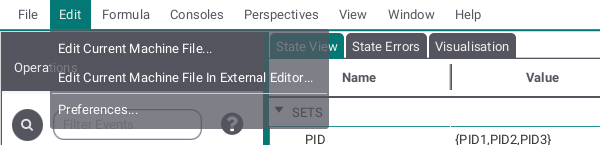
The Edit submenu provides two ways to edit the current machine (either in the editor provided by the ProB2-UI or in the your operating systems standard editor) and allows to edit your general and global preferences by opening a seperate window.
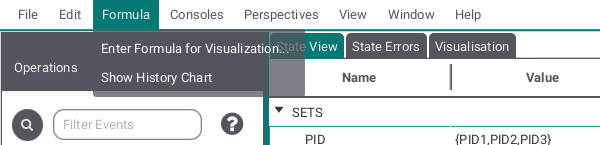
Here you can add formulas for visualization and open the history chart window.
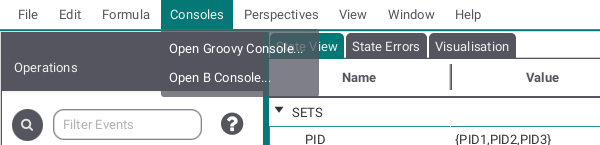
This submenu leads to two consoles, one Groovy, one B.
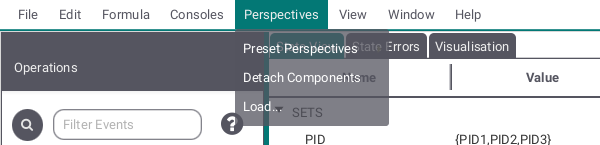
The Perspectives submenu allows you to change the appearance of the main view. The default view is shown at the top and two additional perspectives (Seperated History and Seperated History and Statistics) are preset. By Detach Components the view can be shown in seperate windows. Load allows you to make your own perspective by providing an FXML file containing the views but be aware that this might ruin the ability to detach components.
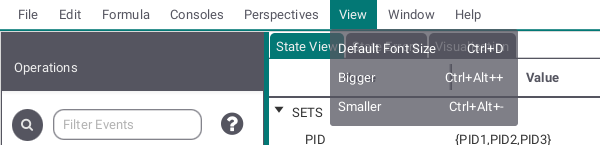
This submenu allows you to adjust font and button size in the ProB2-UI.
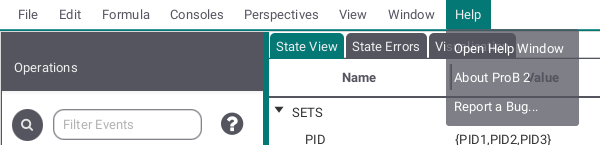
The Help submenu provides you with help about the ProB2-UI, information about the ProB2 UI, ProB2 kernel, ProB CLI and Java version used here and a way to report issues regarding the ProB2-UI.
History View
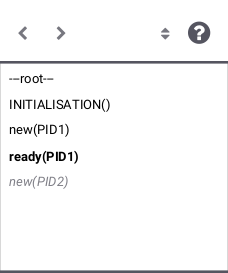
The History View shows a list of already executed operations. The items contained in this list are linked to the State View: When selecting one of these items, State View shows the current and the previous state of the chosen machine. The chrevron buttons on the left allow to go back and forth in history by one step. The two buttons on the right provide sorting and help.
Note that if you choose to go back in history and execute an operation the previously following one will be lost.
Project View
If no machine or no project has been opened, the Project View will allow you to create a project. If you choose to open a machine without having a project, a default project will be created.
The Project View contains several tabs:
- Project, containing name and description
- Machines, containing machines added to this project
- Verifications, containing the verification status of each machine
- Preferences, containing custom preferences
- Run Configurations, containing machines paired with preferences (each pair has its own entry)
Project Tab
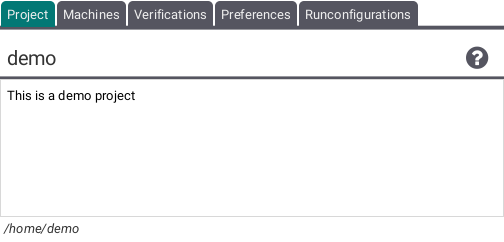
This tab shows the name and the description of the current project. Both are either automatically generated by opening a machine or chosen by the user who manually created the project and can be changed by double clicking on each respectively.
Machines Tab
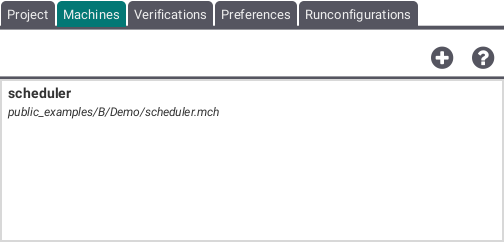
This tab shows the machines belonging to the project. By using the plus button several machines can be added to the project. By clicking right on a specific machine this machine can be edited or removed from the project.
Verifications Tab
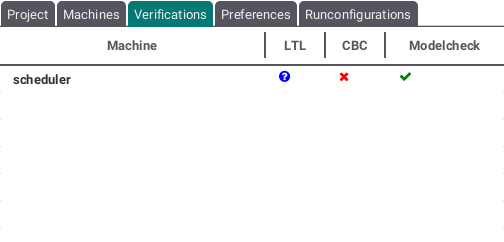
This tab shows the status of each type of verification run on the machines contained by the project. If no test of a specific verification type has been run, a blue questionmark sign is shown. If the verification type could not recognize any failures, a green check will be displayed. If a test failed, a red x sign will be shown.
Preferences Tab
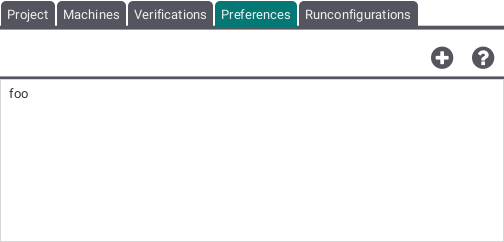
This tab allows to add, edit and remove preference settings and shows a list of these preference settings by the names chosen by the user. By pressing the plus button you can add and by right clicking on a specific preference setting you can edit and remove.

The screenshot above shows the window for adding and editing preferences.
Run Configurations Tab
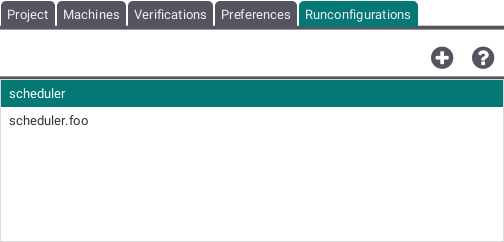
This tab allows to pair up machines and preferences. The machine running with default preferences will be displayed just by name. Run configurations combining a machine with a custom preference setting are shown as machinename.preferencename.
Verification View
The Verification View provides 3 different methods to test a machine:
- Modelchecking
- LTL Verifications and
- Constraint Based Checking
In each tab you can add multiple tests to check you currently selected machine and interrupt the checking process by pressing the "Cancel" button.
Modelchecking
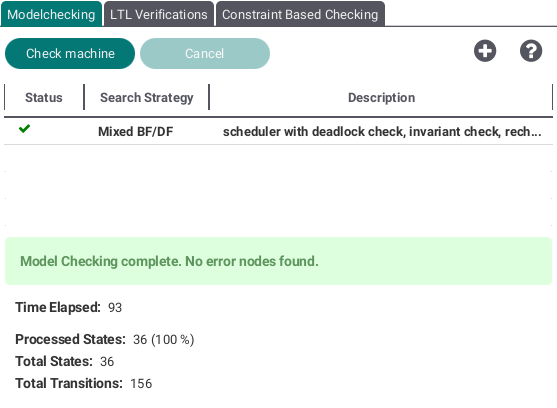
By pressing the plus button you can add several model checking variants. The following view will be shown:
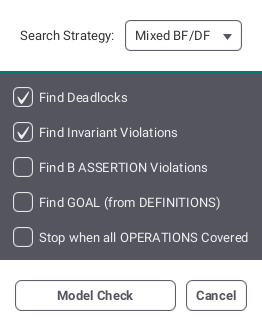
Select one of the search strategies (breadth first, depth first or a mix of both) and the checkboxes containing different possible errors like deadlocks to be checked for. By pushing the "Model Check" button your selected variant will be added to the list shown at the top of the Modelchecking Tab.
LTL Verifications
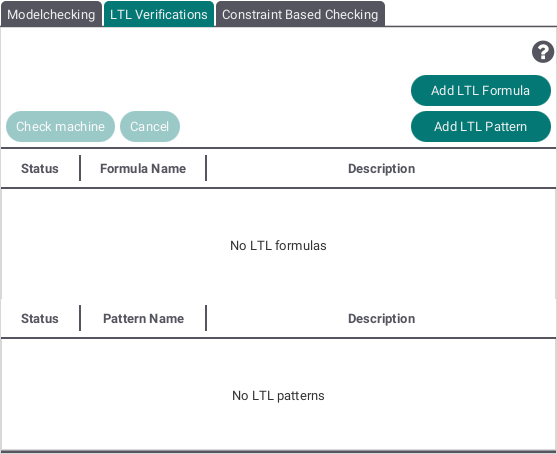
By pressing the "Add LTL Formula" or "Add LTL Pattern" buttons an editor for each respectively will be opened and you can add LTL formulas or patterns to the lists to be checked for.
Constraint Based Checking
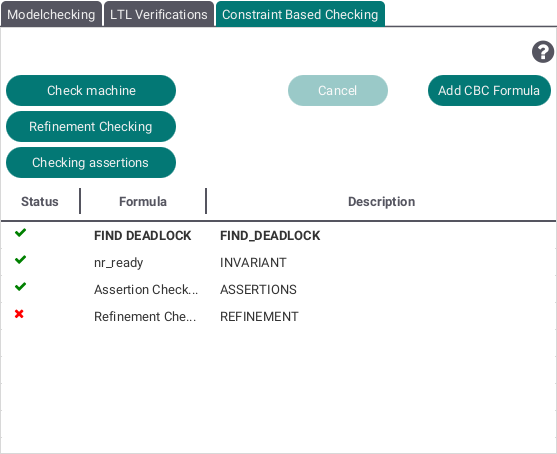

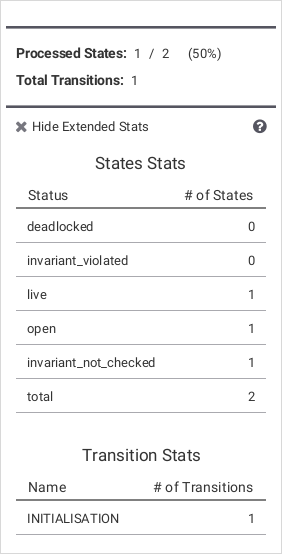
Statistics View
The Statistics View provides some state and transition data: The main view shows the quantity of processed states and total transitions, the extended view shows additional state and transition statistics