Eval Console
For this tutorial, load for example the file StackConstructive.mch included in the examples/Tutorial directory of the ProB distribution (this example is also discussed in the Tutorial Modeling Infinite Datatypes).
After loading the file, double click on the green line "SETUP_CONSTANTS" in the "Enabled Operations" pane. Now double click on the green "INITIALISATION" line in the same pane. To start the "Eval..." interactive console you can either
- use the "Eval..." command in the Analyse menu,
- double-click any line in the "State Properties" pane or
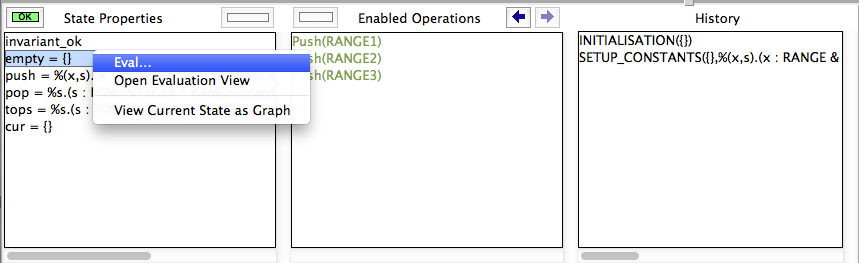
- right-click (Control-Click on a Mac) on the "State Properties" pane and select the "Eval..." entry as shown below:
This will bring up a new window, the "Eval Console":
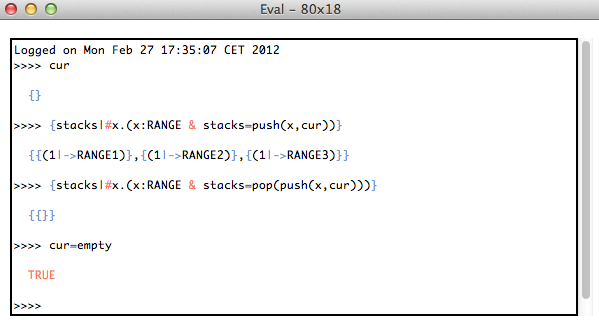
You can now enter predicates or expressions and hit return or enter to evaluate them in the current state of the machine. Below is a small transcript:
You can use the up and down arrow keys to navigate to earlier predicates or expressions you have entered.
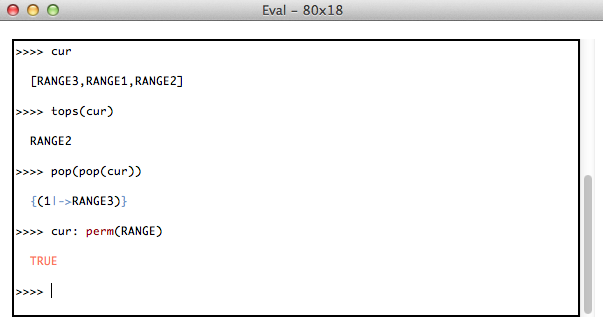
If you change the state, then the expressions and predicates are evaluated in that state. For example, if you execute the operations Push(RANGE3), Push(RANGE1), Push(RANGE2) by double-clicking on the respective lines in the "Enabled Operations" pane, then a transcript of using the console is as follows:
The console works the same way for Event-B models, Z and TLA specifications. However, in all those cases the Eval console uses the classical B parser and you have to use classical B syntax for entering predicates or expressions. The console also works in CSP mode and uses a CSP parser there.
As of version 1.4 the console allows defining new local variables (local to the console) using Haskell's let syntax: let id = Expr. You can use the :b command to browse your let definitions. Here is an example session:
>>> let x = 2**10
1024
>>> let y = x+x
2048
>>> :b
x = 1024
y = 2048
>>> {v| v>x & v<y & v mod x = 1}
{1025}
>>>
A similar console is also available for the command-line version of ProB (probcli) using the -repl command. More details are available on the separate wiki page for probcli.
We now also have made two versions of a ProB Logic Calculator available online. The second one works similarly to the Eval console above, but is not linked to any B machine. You can try it out directly on this page below: