Tutorial Setup Phases
We assume that you grasped the first steps of opening and animating a B machine as outlined in Tutorial First Steps.
In this lesson, we examine more closely the various steps that ProB undertakes before a machine can be animated.
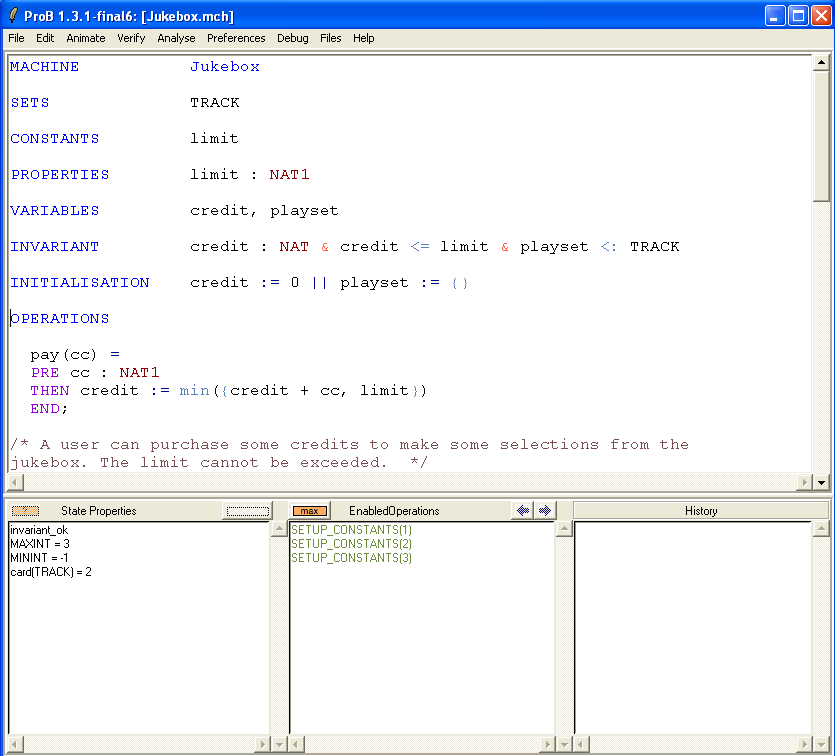
First, open the machine "Jukebox.mch" which can be found in the SchneiderBook/Jukebox_Chapter13 subdirectory of the ProB Examples folder. The main ProB window should look more or less as follows:
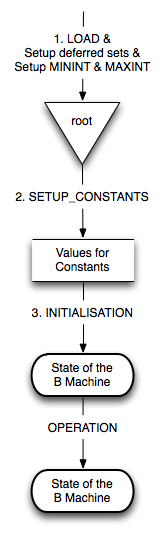
In general, before the operations of a machine can be applied, ProB needs to traverse three phases:
- 1. Loading the machine and determining the sizes of the deferred sets, as well as fixing the values of MININT and MAXINT.
- 2. Setting up the constants of the machine, such that the PROPERTIES and CONSTRAINTS are satisfied.
- 3. Performing a valid initialisation of the machine.
This process is illustrated in the following picture:
We now examine these phases on the Jukebox machine in more detail
1. Loading
Here ProB parses and type checks the machine.
Then it will fix the values of MININT and MAXINT. There are two ways you can influence this:
- by using "Animation Preferences..." command in the "Preferences" menu and modifying the corresponding preferences.
- by including a "DEFINITIONS" section in your machine (if there is not yet one) and then adding a definition of the form SET_PREF_MAXINT == 5 or SET_PREF_MININT == -2147483648.
Note that these preferences determine the elements of the sets INT (implementable integers), NAT (implementable natural numbers) and NAT1. In addition, they are used to control the enumeration of variables of type INTEGER</tt) (mathematical integers), in case a definite value cannot be inferred from the machine.
Afterwards, ProB will determine the cardinality of all deferred sets (such as TRACK in the Jukebox machine).There are several ways you can influence this:
- by using "Animation Preferences..." command in the "Preferences" menu and modifying the preference "Size of unspecified deferred sets in SETS section".
- by including a "DEFINITIONS" section in your machine (if there is not yet one) and then adding a definition of the form scope_TRACK == 5 (where TRACK is the name of the deferred set you wish to influence and 5 is its desired cardinality). This will override the default size.
- by including a predicate of the form card(TRACK)=5 in the PROPERTIES or CONSTRAINTS section of your machine.
As you can see above, ProB has chosen MAXINT=3, MININT=-1 and card(TRACK)=2.
2. SETUP_CONSTANTS
In this phase ProB will try and find values for the constants and parameters of your machine, so that the PROPERTIES and CONSTRAINTS are true. Note that ProB will not (yet) modify the settings from phase 1 for MAXINT, MININT and the size of the deferred sets.
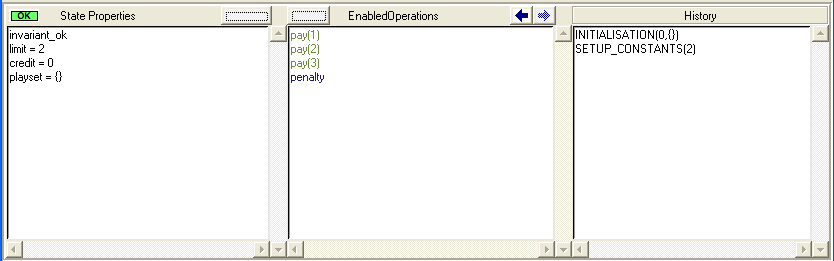
ProB will initiate this phase automatically, and as we can see above, ProB has found three distinct ways to setup the constant limit. By double clicking on "SETUP_CONSTANTS(2)" we proceed to the next phase:
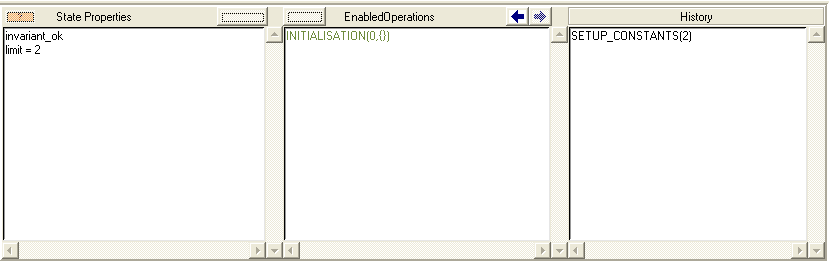
3. INITIALISATION