Tutorial Model Checking, Proof and CBC: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
Indeed, all reachable states are correct, in the sense that the invariant counter:NATURAL & counter<=128 holds for all of those states. | Indeed, all reachable states are correct, in the sense that the invariant <tt>counter:NATURAL & counter<=128</tt> holds for all of those states. | ||
[[file:DoubleCounterStatespace.png|center]] | |||
However, you will not be able to prove the system correct using AtelierB or Rodin. | |||
== Constraint Based Checking (CBC) for the Invariant == | |||
[[file:CBCDoubleCounter1.png|center]] | |||
[[file:CBCDoubleCounter2|center]] | |||
Revision as of 12:36, 1 March 2011
We assume that you have completed Tutorial Complete Model Checking.
Let us examine the following B machine:
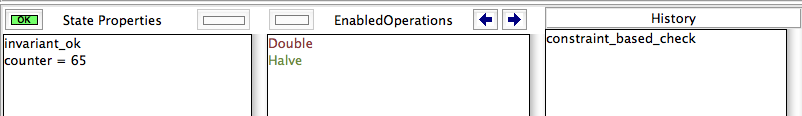
MACHINE DoubleCounter VARIABLES counter INVARIANT counter:NATURAL & counter<=128 INITIALISATION counter:=8 OPERATIONS Double = PRE counter<100 THEN counter := 2*counter END; Halve = BEGIN counter := counter/2 END END
Now click the "Model Check" button. After a short while, ProB will give you the following message:
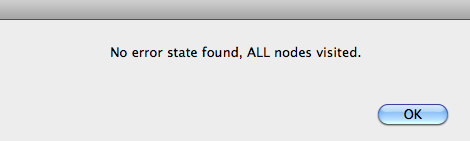
Is this model correct?
If you look purely at the state space of the machine (choose the View State Space command in the Animate menu) you get the following picture:
Indeed, all reachable states are correct, in the sense that the invariant counter:NATURAL & counter<=128 holds for all of those states.
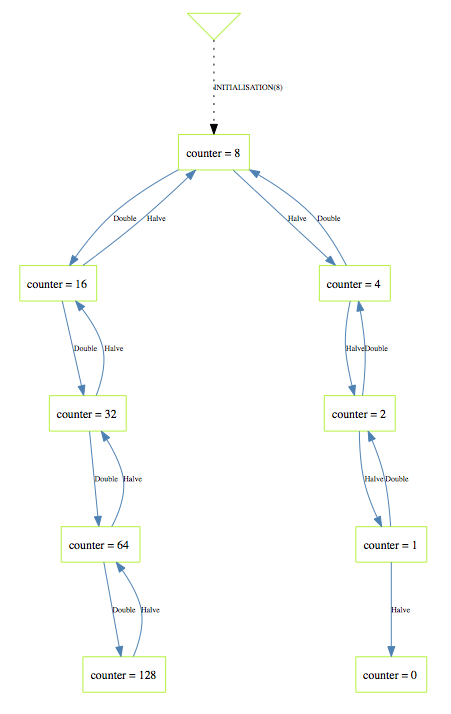
However, you will not be able to prove the system correct using AtelierB or Rodin.
Constraint Based Checking (CBC) for the Invariant